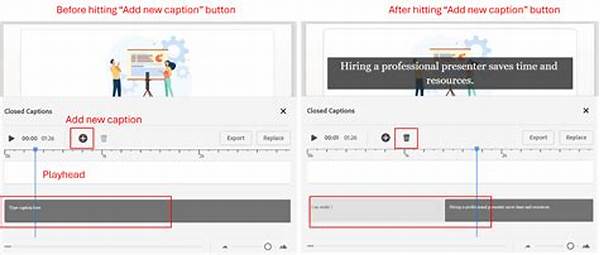
The study of history has long been considered a discipline rooted in the meticulous examination of primary sources and narratives passed down through the ages. However, the advent of technology and computational techniques has ushered in a paradigm shift. Computational methods in history studies are revolutionizing the way historians conduct research, analyze data, and interpret past events. By applying advanced algorithms, data mining, and digital tools, researchers are uncovering patterns and insights that were once hidden within the vast expanse of historical data.
Read Now : Unified Project Collaboration Systems
The Role of Big Data in Historical Analysis
In recent years, the integration of computational methods in history studies has enabled historians to process large volumes of data with unprecedented efficiency. This transformation is not merely about digitizing archives but rather involves the sophisticated analysis of massive datasets. With the help of computational tools, historians can identify trends, connections, and anomalies that traditional methods might overlook. For instance, text analysis and sentiment analysis can reveal societal attitudes and emotional climates during specific historical timelines. By harnessing big data, researchers can reconstruct historical events with greater accuracy and depth.
Beyond quantitative analysis, computational methods in history studies also allow for the visualization of data in ways that make it more accessible and understandable. Maps, charts, and interactive models bring historical narratives to life, enabling both scholars and the public to engage with history dynamically. These visual tools not only illustrate complex relationships but also encourage further exploration and inquiry, thereby deepening our understanding of the human past.
Enhanced Research Techniques
1. Digital archives have revolutionized access to historical documents, embodying computational methods in history studies.
2. Text mining and natural language processing enhance understanding of historical texts through computational methods in history studies.
3. Geographical information systems (GIS) reveal spatial patterns in historical data, a notable advancement in computational methods in history studies.
4. Network analysis uncovers historical relationships and connections, demonstrating the power of computational methods in history studies.
5. Simulation models test historical scenarios and hypotheses, an innovative aspect of computational methods in history studies.
Bridging Traditional and Modern Approaches
Despite their transformative potential, computational methods in history studies should not be viewed as a replacement for traditional historical research. Instead, these tools complement established methodologies, offering new perspectives and enhancing the historian’s toolkit. By bridging traditional approaches with modern technology, historians can construct richer, multi-dimensional narratives that account for previously unexplored variables.
A critical aspect of integrating computational methods in history studies is the collaboration between historians and data scientists. Each brings crucial expertise to the table, with historians providing contextual knowledge and interpretive skills, while data scientists contribute technical proficiency in handling complex datasets. Together, they forge new pathways for historical inquiry, ensuring that technology serves to augment rather than overshadow the nuanced understanding of the past.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
1. Ensuring data accuracy is paramount when employing computational methods in history studies.
2. Addressing bias in algorithms is critical to maintain objectivity in computational methods in history studies.
3. The digital divide poses a barrier to accessing computational tools, a challenge for computational methods in history studies.
4. Balancing data privacy with open access raises ethical concerns in computational methods in history studies.
5. The potential over-reliance on technology can overshadow traditional analysis in computational methods in history studies.
6. Preserving digital data for future research is essential in the realm of computational methods in history studies.
7. Acknowledging the expertise of both historians and data scientists fosters collaboration in computational methods in history studies.
Read Now : Creating Effective Story Subplots
8. Educating historians on computational techniques expands the utility of computational methods in history studies.
9. Recognizing the limitations of computational tools ensures a balanced application in history studies.
10. Emphasizing critical thinking remains a priority alongside computational methods in history studies.
Integrating Computational Tools with Historical Scholarship
The emergence of computational methods in history studies has prompted scholars to reassess their approach to historical research. By incorporating digital tools and methodologies, the discipline is evolving to meet the demands of a data-rich world. Digital archives and software designed specifically for historical analysis are reshaping the field, enabling researchers to delve deeper into the past with enhanced precision.
However, this integration requires historians to adapt to new skill sets, merging traditional scholarship with technical acumen. Training programs and courses now emphasize the importance of acquiring proficiency in digital tools while maintaining a firm grasp of historiographical methods. As computational methods in history studies become more prevalent, the ability to analyze data holistically and critically becomes indispensable. This synthesis of skills is cultivating a new generation of historians equipped to navigate a digital landscape while upholding the scholarly rigor of traditional historical research.
Fostering a Collaborative Research Environment
Collaboration lies at the heart of effectively utilizing computational methods in history studies. Historians are increasingly working alongside computer scientists and data analysts to harness the full potential of technology in unraveling historical complexities. This interdisciplinary approach fosters a vibrant exchange of ideas, encouraging the creation of innovative research initiatives that reflect a multitude of perspectives.
Moreover, funding bodies and academic institutions are recognizing the value of such collaborative efforts, providing resources and platforms for joint projects. By fostering an environment that encourages cross-disciplinary collaboration, the impact of computational methods in history studies is amplified, ensuring that historical research remains relevant and insightful in an ever-evolving digital age.
Future Directions for Computational Methods in History Studies
As the field of history continues to embrace technological advancements, the potential for future developments in computational methods in history studies is vast. Machine learning and artificial intelligence promise to further revolutionize the way historical data is processed and interpreted. These technologies can identify complex patterns, predictive models, and anomalies across large datasets, offering historians new avenues for exploration and discovery.
Furthermore, as digital tools become more sophisticated and accessible, historians have the opportunity to engage with a broader audience. Public history initiatives and online platforms facilitate the sharing of digitally-driven insights, fostering an engaged and informed public discourse on historical topics. By leveraging computational methods in history studies, scholars can bridge the gap between academia and the public, ensuring that historical knowledge is not only preserved but also made relevant and accessible in the digital age.
As digital transformation continues to shape the landscape of historical research, ongoing dialogue and innovation remain essential. By integrating computational methods in history studies, historians are not only enhancing their ability to explore the past but are also ensuring that history retains its significance and resonance in the present and future.
Implications for Teaching and Learning with Technology
Incorporating computational methods in history studies also holds transformative potential for education. As digital literacy becomes increasingly important across disciplines, history education is adapting by integrating technology into its curricula. Digital history projects, interactive timelines, and online collaborations provide students with hands-on experiences in analyzing historical data through computational tools.
Educators are tasked with teaching students not only the technical skills required for such analyses but also fostering critical thinking and interpretative skills. By emphasizing the interplay between digital methods and traditional historical inquiry, students are better prepared to navigate the complexities of modern historical research. This approach ensures that future historians are well-equipped to contribute meaningfully to both academia and society at large, continually enriching our collective understanding of the past through computational methods in history studies.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the introduction of computational methods in history studies represents a significant evolution in the discipline. While challenges and ethical considerations accompany this transition, the benefits are abundant, offering historians innovative tools to uncover deeper insights into historical phenomena. Collaboration and education are key to realizing the full potential of these methods, ensuring that they complement rather than replace traditional historiography.
Looking ahead, the continued integration of computational methods in history studies promises to expand the boundaries of historical research, paving the way for new discoveries and fostering a more comprehensive understanding of the past. By embracing both technology and traditional methodologies, historians can craft compelling narratives that resonate with present and future generations, ensuring the vitality and relevance of history in a rapidly changing world.